Bookkeeping
Net Realizable Value NRV Formula Example
Other companies may be a little more transparent in how they use NRV in determining their inventory level. As part of its 2021 annual report, Shell reported $25.3 billion of inventory, up more than 25% from the year prior. First, the approach requires substantial assumptions from management about the future of the product. For goods clouded with uncertainty, it may be nearly impossible to predict obsolescence, product defects, customer returns, pricing changes, or regulation. As economies thrive, clients often have more money at their disposal and are able to pay higher prices. Alternatively, when the economy is down, clients may pass on orders or find it more difficult to make full payments.
Detailed Analysis of Net Realizable Value (NRV) with Formula and Examples
In general, US GAAP does not permit recognizing provisions for onerous contracts unless required by the specific recognition and measurement requirements of the relevant standard. However, if a company commits to purchase inventory in the ordinary course of business at a specified price and in a specified time period, any loss is recognized, just like IFRS Standards. If a company has a contract to sell inventory for less than the direct cost to purchase or produce it, it has an onerous contract.
Financial Accounting
Thus, the use of net realizable value is a way to enforce the conservative recordation of inventory asset values. It’s the selling price of an asset less the total cost of selling the asset. To calculate the NRV of receivables, subtract the estimated allowance for doubtful accounts from the gross accounts receivable. For example, if gross receivables are $100,000 and doubtful accounts are $10,000, the NRV of receivables is $90,000.
- A new assessment of net realizable value should be made in each subsequent period.
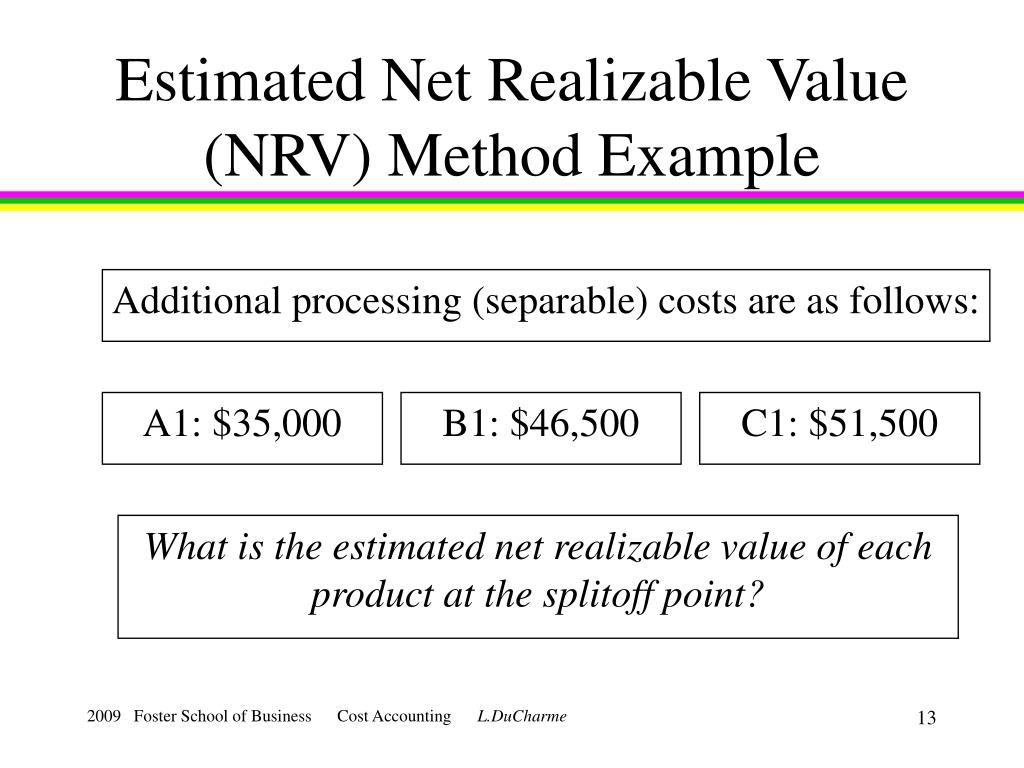
- When using NRV calculations for cost accounting, these expenses are the separable costs that can be identified or allocated to each good.
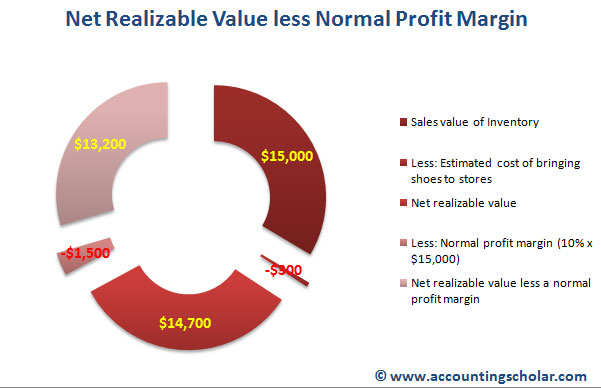
- The cost is still $50, and the cost to prepare it for sale is $20, so the net realizable value is $45 ($115 market value – $50 cost – $20 completion cost).
- By calculating NRV, businesses can prevent overvaluation of assets and provide a truthful representation of their financial health.
- As a result of our analysis, we would write down the cost of Rel 5 HQ Speakers, highlighted below in yellow, by $6,000 so the new cost on our books is $50 each.
- Volkswagen disclosed ownership of €43.7 billion of inventory, a very slight decline from the €43.8 billion of inventory carried at the end of December 2020.
Inventory Measured Using Any Method Other Than LIFO or the Retail Inventory Method
Because it is used in several different situations, net realizable values can tell analysts and accountants several important pieces of information. Charlene Rhinehart is a CPA , CFE, chair of an Illinois CPA Society committee, and has a degree in accounting and finance from DePaul University.
Lower of cost or market (old rule)
The net realizable value is defined as the estimated selling price in the ordinary course of business less the estimated costs necessary to make the sale and estimated costs to get the inventory in condition for sale. Other times NRV is used by accountants to make sure an asset’s value isn’t overstated on the balance sheet. If you’re a CPA, you’ll come across NRV within cost accounting, inventory, and accounts receivable. According to the notion of lesser cost or net realizable value, inventory should be recorded at the lower of its cost or the price at which it can be sold. The estimated selling price of something in the regular course of business, less the completion, selling, and shipping costs, is known as the net realizable value. It is accepted in both the accounting standards, GAAP and IFRS to ensure the ending inventory value is neither overestimated nor underestimated.
Unlike IAS 2, US GAAP does not contain specific guidance on storage and holding costs, which may give rise to differences from IFRS Standards in practice. Unlike IAS 2, US GAAP allows use of different cost formulas for inventory, despite having similar nature and use to the company. Therefore, each company in a group can categorize its inventory and use the cost formula best suited to it.
Knowledgeable decision makers understand that some degree of uncertainty exists with all such balances. By including this amount, company officials are asserting that they have obtained sufficient evidence to provide reasonable assurance that the amount collected will not be a materially different figure2. A new assessment of net realizable value should be made in each subsequent period.
It is worth noting that the adjustments can be made for each item in inventory or for the aggregate of the entire net realizable value inventory to the lower cost or NRV. Once curtailed down, the inventory account becomes the new basis for reporting purposes and valuation. As part of this filing, Volkswagen disclosed the nature of the calculation of its inventory. In compliance with prevailing accounting regulation, Volkswagen considered net realizable value when determining its inventory value. Different companies may be exposed to different risks and business impacts that are factored into NRV calculations differently. For example, certain industries may necessitate dealing with customers that have riskier credit profiles, thus forcing the company to experience larger write-off allowances.
An accounts receivable balance is converted into cash when customers pay their outstanding invoices, but the balance must be adjusted down for clients who don’t make payments. NRV for accounts receivable is calculated as the full receivable balance less an allowance for doubtful accounts, which is the dollar amount what are education tax credits of invoices that the company estimates to be bad debt. A company may have a decommissioning or restoration obligation to clean up a site at a later date, which must be provided for. Accordingly, these decommissioning and restoration costs are recognized in profit or loss when items of inventory have been sold.
Instead, such costs are added to the carrying amount of the related property, plant and equipment. The subsequent depreciation of the cost is included in production overheads in future periods over the asset’s estimated remaining useful life. Like IAS 2, US GAAP companies using FIFO or the weighted-average cost formula measure inventories at the lower of cost and NRV. Unlike IAS 2, US GAAP companies using either LIFO or the retail method compare the items’ cost to their market value, rather than NRV.
Net realizable value (NRV) is used to determine whether it’s worth holding on to an asset or not. However, the company anticipates that it will incur a collection cost of $200 and may not be able to collect $300 of the invoice amount due to potential bad debt. In this blog, we will explain the concept of NRV, how to calculate it, and provide examples to illustrate its application.